Individual and Family
What is Self-Employed Health Insurance?
Published on December 12, 2024
Share
Key Takeaways:
- Self-employed individuals can choose health insurance through various options, including ACA Marketplace plans, spousal plans, Medicaid, and trade organization memberships.
- Balancing cost with coverage needs is essential, as premiums, deductibles, and out-of-pocket limits vary across different plans.
- Flexible coverage, like high-deductible plans, can be beneficial for those with changing incomes, while short-term insurance may fill temporary gaps.
Understanding Health Insurance for Self-Employed
When you’re self-employed, whether a freelancer, gig worker, or small business owner, health insurance isn’t automatically provided. Instead, you’ll need to explore options like the Health Insurance Marketplace, private insurers, or group plans through professional associations.
Health insurance provides peace of mind, covering unexpected medical expenses and offering access to preventive and mental health services. Although the costs can feel high, having health insurance can be essential for financial stability, allowing you to stay healthy and manage expenses.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing a Plan
Coverage Needs
Start by considering what type of healthcare you may need, like routine doctor visits, prescriptions, or special services. Health plans typically fall into two categories:
- Basic Coverage: Covers essentials like preventive care and emergency visits, with lower premiums but fewer benefits.
- Comprehensive Coverage: Offers more extensive access to specialists and additional benefits, with higher premiums.
Also, pay attention to network restrictions, which can impact your choice of providers and out-of-pocket costs.
Affordability
Review not only the monthly premiums but also other costs like deductibles, co-pays, and coinsurance. If you’re looking at high-deductible plans, a Health Savings Account (HSA) can help cover medical expenses with pre-tax savings.
Flexibility
Self-employed income can vary, so a flexible health plan might suit your situation better. High-deductible health plans (HDHPs) offer lower premiums for people with minimal healthcare needs, while short-term health insurance can provide temporary coverage during transitional periods.
Health Insurance Options for Self-Employed Individuals
ACA Marketplace Plans
The ACA Marketplace provides self-employed individuals with access to health insurance that meets federal standards. These plans include:
- Comprehensive Coverage: All plans cover essential health benefits, like hospitalization, prescriptions, and mental health care.
- Income-Based Subsidies: Many self-employed individuals qualify for subsidies to lower premiums based on income.
- No Medical Underwriting: Coverage eligibility doesn’t depend on your health history.
- Enrollment Windows: Open Enrollment usually occurs from Nov. 1 to Jan. 15 or during a Special Enrollment Period if you experience a qualifying event.
Coverage Under Your Spouse’s Plan
Spousal coverage allows you to join your spouse’s employer-sponsored health insurance if offered. If your spouse’s employer provides health insurance, you can likely join their plan, as most employer-sponsored health plans include spousal options.
- Enrollment Periods: Enroll during the employer’s open enrollment or a special enrollment period following a qualifying event.
- Special Enrollment Timing: If you lose other coverage, you have a 30-day window to enroll under your spouse’s plan.
Medicaid
Medicaid offers free or low-cost health insurance to qualifying low-income individuals. Self-employed individuals may be eligible if they meet income guidelines.
- Eligibility: In most states, adults with household income up to 138% of the federal poverty level qualify.
- Enrollment Flexibility: Apply anytime, with coverage adjusting to income changes.
- Considerations for Older Adults: Medicaid estate recovery may impact estates of beneficiaries 55 and older in some states.
COBRA (Consolidated Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act)
COBRA allows you to temporarily continue a previous employer’s health coverage if you leave a job with group insurance. This option keeps you covered but usually comes with higher costs, as you’ll pay the full premium.
- Duration: COBRA can extend your coverage for up to 18 or 36 months, depending on your situation.
- Continuation of Benefits: Retain any paid deductibles and out-of-pocket maximums.
- Higher Costs: You’ll pay the full premium (your share and the employer’s), plus a 2% administrative fee, making it more expensive than employer-sponsored coverage.
Health Insurance Through Trade Organizations
Trade organizations may provide access to health benefits or discount programs for members. Some trade associations or professional groups offer health benefits, though coverage quality varies.
- Types of Plans: Options may include ACA-compliant Marketplace plans, short-term plans, or medical discount programs that may not technically be insurance.
- ACA Protections: Review the coverage details carefully to confirm if it includes essential health benefits or is eligible for subsidies.
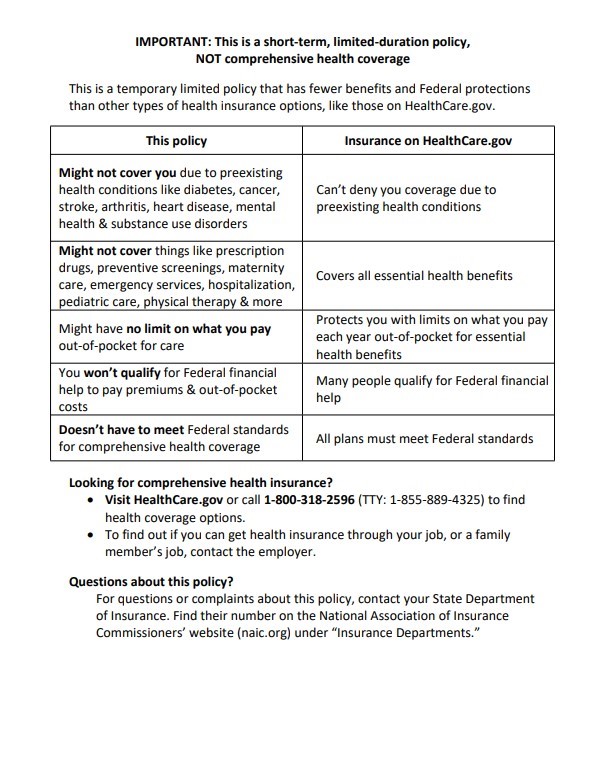
Short-Term Health Insurance
Short-term health insurance offers temporary coverage for short gaps but is not ACA-compliant. Short-term health insurance can fill temporary gaps but doesn’t provide comprehensive coverage.
- Limited Duration: New rules limit coverage to a maximum of four months, including renewals.
- Coverage Gaps: Short-term plans lack essential health benefits and often exclude pre-existing conditions.
- Temporary Solution: Use short-term plans if you miss ACA open enrollment and don’t qualify for a special enrollment period.
Cost of Health Insurance for Self-Employed Individuals
Here’s a breakdown of average costs for self-employed health insurance options:
| Plan Type | Average Monthly Premiums | Average Deductible | Out-of-Pocket Maximum | Co-pays |
| ACA Marketplace Plan | Average Benchmark Premium: $497 | Individual: $4,364 Family: $8,439 | Individual: $9,200 Family: $18,400 | Typically $25–$50 per visit |
| Private Plan | Varies widely* | Varies, often higher | Often higher than ACA | Typically $30–$60 |
| Short-Term Plan | $74 per month | Higher than ACA/private | Typically no limit | Typically full payment due |
*Private plan costs vary widely depending on coverage, insurer, and health factors. Short-term plans offer lower premiums but often come with limited coverage, higher deductibles, and no set out-of-pocket maximums. The information above was updated for 2024.
Factors Affecting Cost
Premium costs often depend on your age, location, tobacco use, and income. ACA plans offer subsidies to eligible individuals based on income, which can help make health insurance more affordable.
To minimize health insurance expenses, consider these strategies:
- Apply for Subsidies: Qualify for ACA subsidies to reduce premium costs.
- Use HSAs: For high-deductible plans, contribute to Health Savings Accounts to cover expenses with pre-tax dollars.
- Shop During Open Enrollment: Compare plans annually during open enrollment to secure the best rates and suitable coverage.
How to Enroll in Health Insurance as a Self-Employed Individual
Enrollment Periods
- Open Enrollment Period: Annual window to sign up for health insurance, typically from November 1 to December 15.
- Special Enrollment Period: Opportunity to enroll or change plans due to life events such as marriage or job loss. Self-employed individuals can adjust plans during these times, which are typically available for 60 days following the qualifying event.
Step-by-Step Enrollment Guide
- Evaluate your healthcare needs.
- Determine your budget.
- Compare plan options.
- Collect required documents.
- Enroll through the marketplace, a broker, or insurers directly.
Bringing It All Together
Health insurance is crucial for self-employed individuals, providing financial protection and access to necessary medical care. When selecting a plan, consider your healthcare needs and budget, and make use of open enrollment periods for the best coverage options. Explore your insurance options thoroughly and ensure continuous coverage by enrolling on time.
FAQs
Do I need health insurance as a self-employed individual?
While there is no federal legal requirement or penalty for being uninsured as of 2021, having health insurance is crucial to avoid high medical costs and financial risk associated with unexpected health issues.
Can I deduct health insurance premiums on taxes?
Yes, if you’re self-employed, you can deduct health insurance premiums directly from your income on your tax return, reducing your taxable income and overall tax burden.
What are short-term health insurance options, and are they beneficial?
Short-term health insurance provides temporary coverage for gaps between longer-term plans, like transitions between jobs. While less comprehensive and not covering pre-existing conditions, they can be a cost-effective solution for immediate, short-term health coverage needs.
Does being a freelancer or independent contractor make a difference?
Freelancers and independent contractors qualify for the same health insurance options as other self-employed individuals. They can purchase plans through the ACA marketplace, potentially qualify for subsidies, and use tax deductions for premiums, making individual health insurance plans a viable option.